

The World Bank report has estimated that Maldives will fall into a steep recession with -8.5% growth in 2020, but also forecasts a strong recovery in 2021 with 7.3% growth.
Growth is expected to contract by 8.5 percent in 2020 as the COVID-19 outbreak dampens tourism and construction. As per the report, the current account deficit will improve as remittance outflows and imports decline, more than offsetting the contraction in exports. The decline in capital expenditures is not expected to cover for the loss in tourism revenues, leading to an increase in fiscal deficit and public debt. Poverty is expected to increase as livelihoods are heavily linked to tourism and fisheries.
According to the report, most affected in South Asian region is the Maldives, where tourism directly and indirectly contributes two-thirds of GDP, 80 percent of exports and 40 percent of revenues. A contraction of the economy between 8.5 and 13.0 percent is expected in 2020. With population growth of 1.8 percent in 2019, the per-capita income loss will be significant.
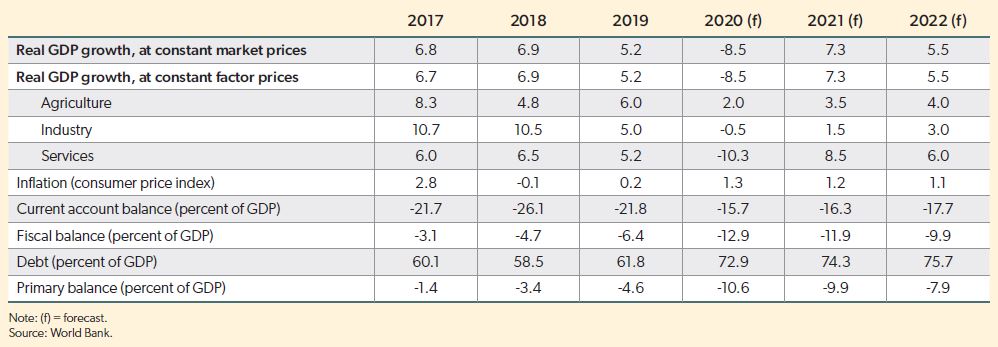
Despite the slump in tourism and related services exports, the current account balance is projected to improve to 15.7 percent of GDP, as remittance outflows and imports related to construction, fuel and tourism decline. The fiscal deficit is projected to double to 12.9 percent of GDP as tourism-related revenues plummet further. Although income taxes will be collected for the first time in 2020, the amount is unlikely to make a significant impact in the current environment.
The government has pledged to cut expenditure by MVR 1 billion (equivalent to 1.2 percent of GDP) to address the revenue shortfall, and to reallocate resources to the health sector, and economic relief for affected households and businesses. Central government debt is expected to rise to 72.9 percent of GDP by end-2020 as the government seeks new sources of external financing to cover the fiscal gap.